Add a SQLite database to your app
This tutorial guides you through connecting a SQLite database to your Webflow Cloud app, defining your schema, and building API routes to store and retrieve user data.
What you’ll learn:
- How to add a SQLite database to your Webflow Cloud project
- How to define and manage your schema with Drizzle ORM
- How to run and apply database migrations
- How to create API routes to add and fetch data
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure you have:
- A Webflow Cloud project linked to a GitHub repository
- A Webflow Cloud environment set up
- Node.js 20+ and npm 10+
- Basic familiarity with JavaScript/TypeScript
New to Webflow Cloud?
If you haven’t already, follow the Quick Start guide to set up your project and environment.
Add a SQLite database
Set up a SQLite database so your Webflow Cloud app can store data. This step connects your project to a reliable, easy-to-use SQLite database.
Open your project in your IDE.
Navigate to your project in your IDE, and open the wrangler.json file.
Add Drizzle ORM
Drizzle ORM is a tool that helps you work with your database using JavaScript or TypeScript code, instead of writing raw SQL. It makes it easier to define your database structure, run migrations, and interact with your data safely and reliably.
Install Drizzle ORM and Drizzle Kit.
Install the required packages for working with Drizzle ORM and managing migrations:
drizzle-orm: The ORM for interacting with your database.drizzle-kit: CLI for migrations and schema generation.tsxandbetter-sqlite3: Required for local development and SQLite support.
Create a schema
A database schema defines the data your app can store. Here, you’ll set up your first table to keep things organized as your project grows.
Create the schema directory.
To keep your schema organized, create a db/schema folder inside your src directory to hold all your schema files.
Define your first table.
Create an index.ts file in src/db/schema Import the necessary Drizzle ORM methods use them to define a usersTable:
This code defines a usersTable with multiple fields.
By defining your schema in code, you ensure your database structure is always documented and version-controlled. To learn more about defining schemas with Drizzle ORM, see the Drizzle ORM documentation.
Initialize the database
Whenever you change your schema, you need to generate a migration. A migration is a set of instructions for updating the database structure. Migrations let you evolve your database structure safely over time, without losing data or breaking your app.
Since you just created a new table, you need to generate a migration file to update the database. In your terminal, run the following commands to generate a new migration file in the drizzle directory from your schema defined in src/db/schema/index.ts, and apply it to the local database:
Connect to the database
Now you’ll connect your app to the database. This makes it easy to add, find, and update information as your users interact with your app.
Create a helper function to get the database instance.
To avoid repeating connection logic, create a reusable helper that returns a Drizzle ORM instance. This ensures you always use the correct schema and environment, and improves performance by reusing connections.
In src/db, create a getDb.ts file and add the following code:
Astro
Next.js
Create a route to add users to the users table.
To allow your app to add new users, create an API route that accepts user details and inserts them into the usersTable. This pattern is common for building RESTful APIs and helps keep your data layer organized.
Astro
Next.js
In src/pages/api, create a users.ts file with the following code:
What’s happening?
- The route receives a POST request with user data.
- It inserts the data into the
usersTable. - On success, it returns the new user; on error, it returns a failure message.
Create a route to get users from the users table.
To retrieve data, create a GET route that returns all users from the database.
Astro
Next.js
In the same users.ts file, add:
What’s happening?
- The route receives a GET request.
- It queries all users from the database.
- Returns the list of users or an error message.
Test your routes.
Test your API routes to make sure you can add and retrieve users from your database.
-
Start your app by running the following command in your terminal:
-
Add a user by sending a POST request (replace
<YOUR_PORT>with your actual port number, for example,4321):A successful response returns the new user as JSON, for example:
Try adding more users with different data to populate your database.
-
Retrieve all users by sending a GET request:
You should see a list of users in the response.
Deploy and view your app
When you deploy to Webflow Cloud, your database migrations are applied automatically and your remote database is updated. From here, you can connect to your database through your app’s endpoints, and any data you add will persist. You can also view and manage your data directly in the Webflow Cloud UI.
Deploy your app.
Use the Webflow CLI to trigger a new deployment of your app. Additionaly, you can commit and push your changes to your GitHub repository to trigger a new deployment as well.
View your app and database in Webflow Cloud
-
Open your project’s environment in Webflow Cloud.
-
After your deployment completes, click the “Storage” tab in your environment.
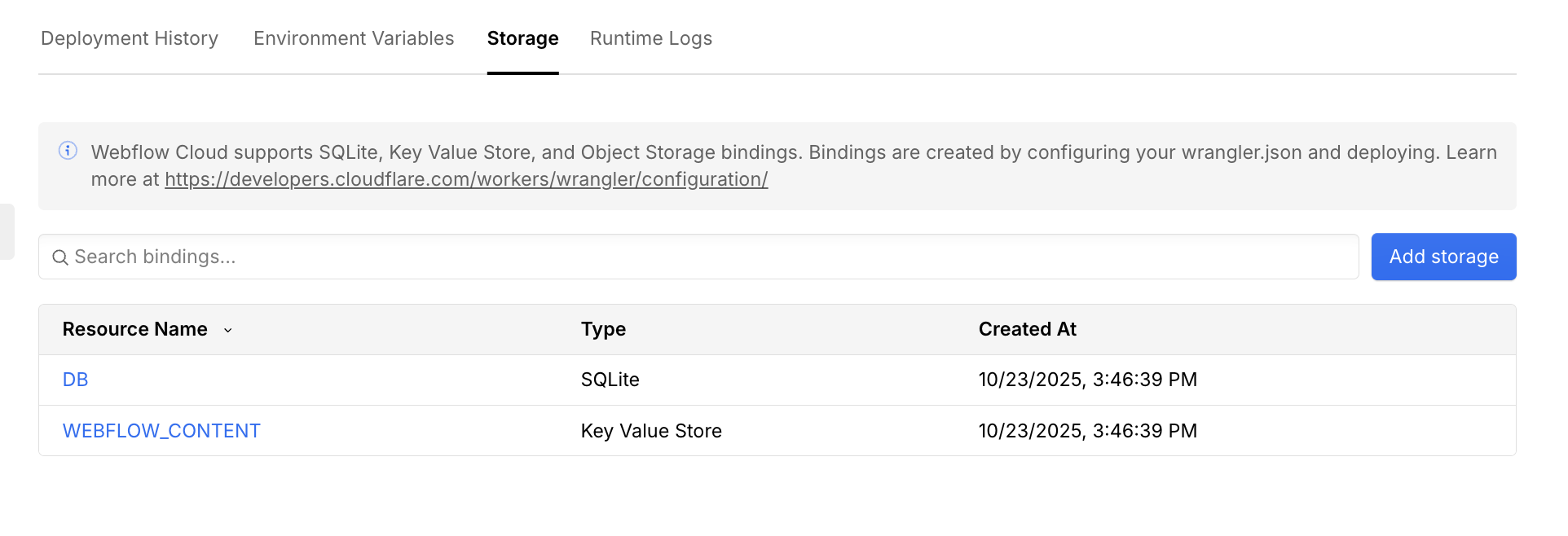
-
Select the
DBbinding to view your database. -
You should see the
users_table. For now, it will be empty, since all the previous changes were local. In the “Storage” tab, you can add and update users through the UI.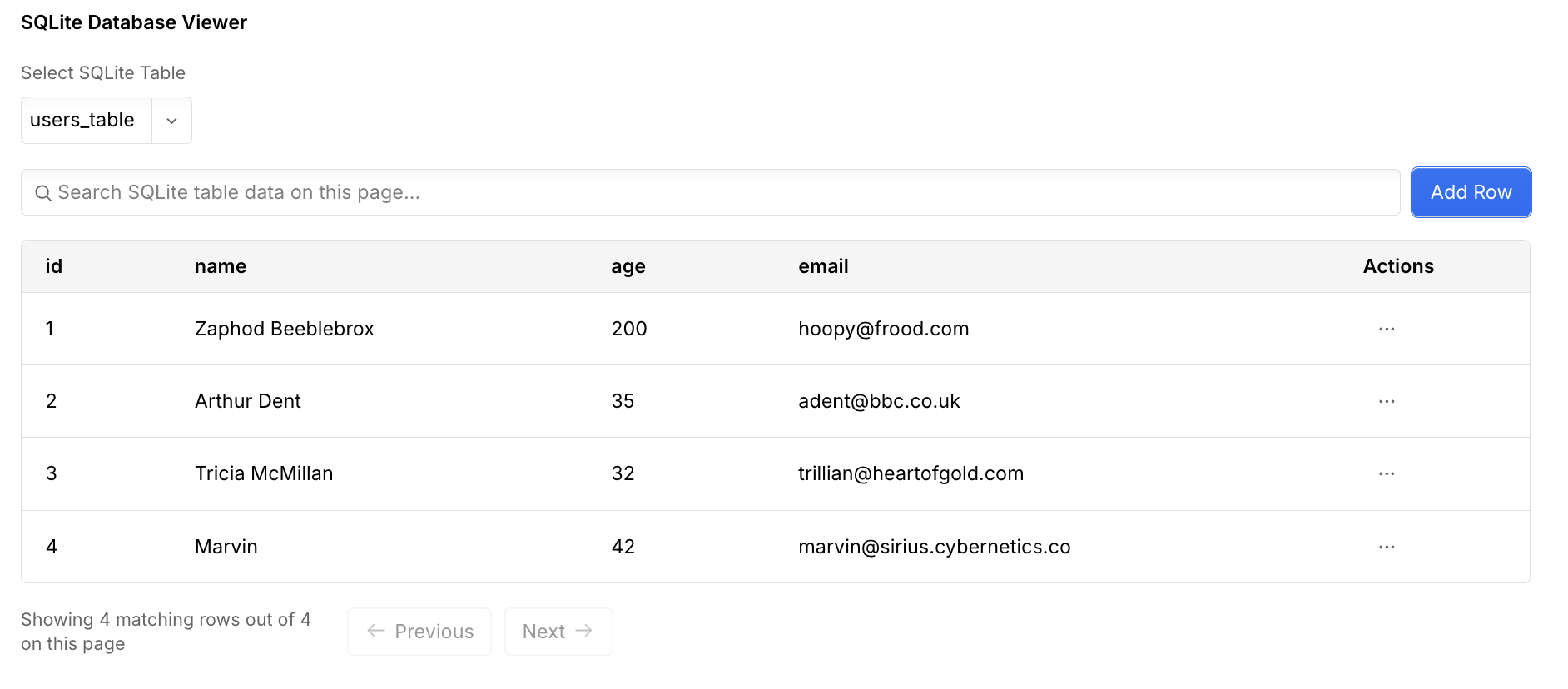
Try calling your API routes
You can also try calling your API routes to add and retrieve users from your deployed app.
You’ve now added persistent storage to your Webflow Cloud app using SQLite and Drizzle ORM. You learned how to:
- Connect a SQLite database to your project
- Define and manage your schema in code
- Run and apply migrations
- Build API routes to add and retrieve data
Next steps
Ready to build more? Check out related guides and resources to keep growing your app’s capabilities.
- Learn more about SQLite in Webflow Cloud
- Learn about other storage options in Webflow Cloud
- See examples for adding authentication to your app