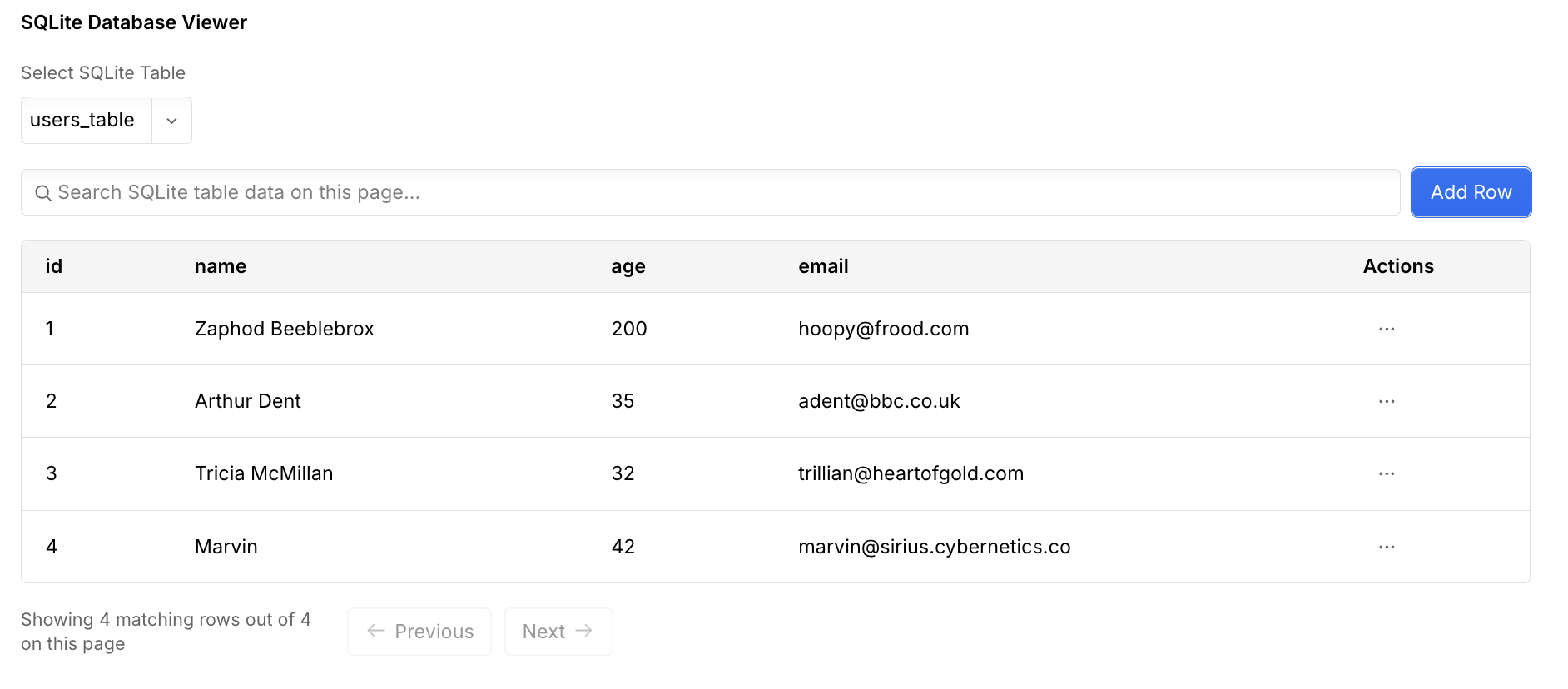
Storing data in Webflow Cloud
Webflow Cloud provides built-in, flexible storage for modern web apps
Webflow Cloud lets you build and deploy modern web applications with built-in support for persistent data storage. Whether you need to store structured records or simple key-value pairs, Webflow Cloud provides flexible options to match your app’s needs.
Storage options in Webflow Cloud
Webflow Cloud offers three storage solutions, each designed for different types of data and use cases:
Best for structured, relational data - like user profiles, product catalogs, or transactional records.
Best for unstructured, dynamic data - like user preferences, session data, or temporary settings.
Best for large files and unstructured data - like images, videos, or PDF files.
How storage works in Webflow Cloud
Webflow Cloud connects your app to storage resources using bindings.
A binding is a configuration that grants your app secure, direct access to a specific resource managed by Webflow Cloud. When you declare a binding in your wrangler.json file and deploy your app, Webflow Cloud automatically creates a resource and grants your app permission to use it.
With bindings, you can:
- Access resources automatically. No secret keys required.
- Reference bindings as environment variables in your app.
- Maintain isolated environments. Each binding is specific to a project’s environment.
- Manage bindings and resources in the Webflow Cloud dashboard.
Bindings combine permission and API access in a single step, so you can read and write data securely and efficiently.
Declaring a binding
Declaring a binding is the first step to using storage in your app. You can declare a binding in the Webflow Cloud dashboard or in your wrangler.json file.
Before you start
Before you can declare a binding, you need to have a project in Webflow Cloud and an environment for your app. If you don’t have a project or an environment, you can create by following the steps in the getting started guide.
Dashboard
wrangler.json
Open the environment dashboard
In Webflow Cloud, select your project and the environment where you plan to deploy your app.
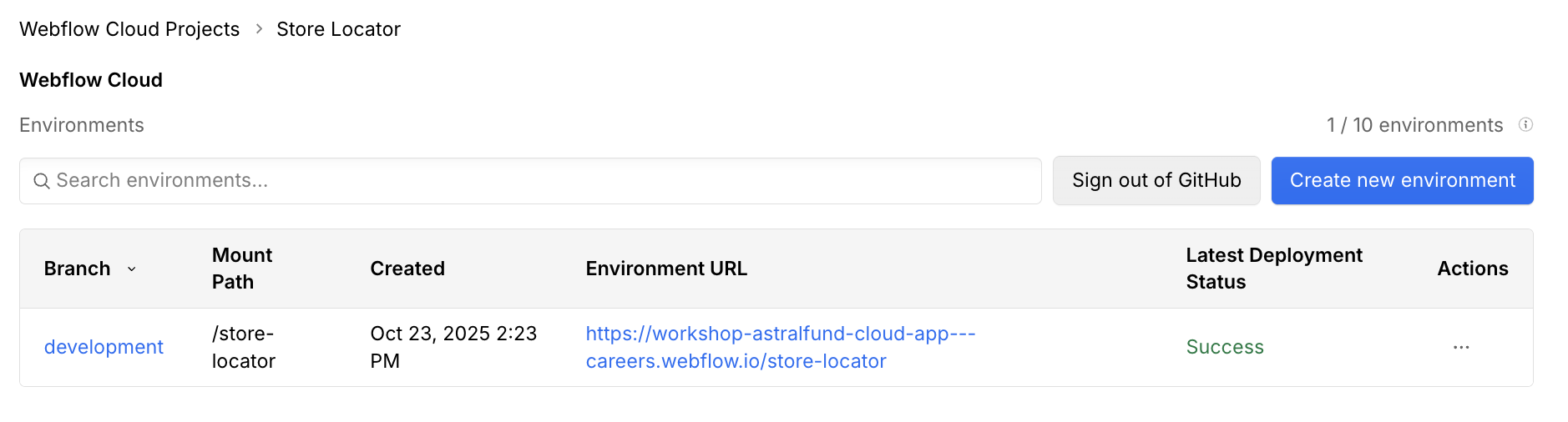
Go to the storage tab
In the environment dashboard, click the Storage tab to view all storage resources for the selected environment.
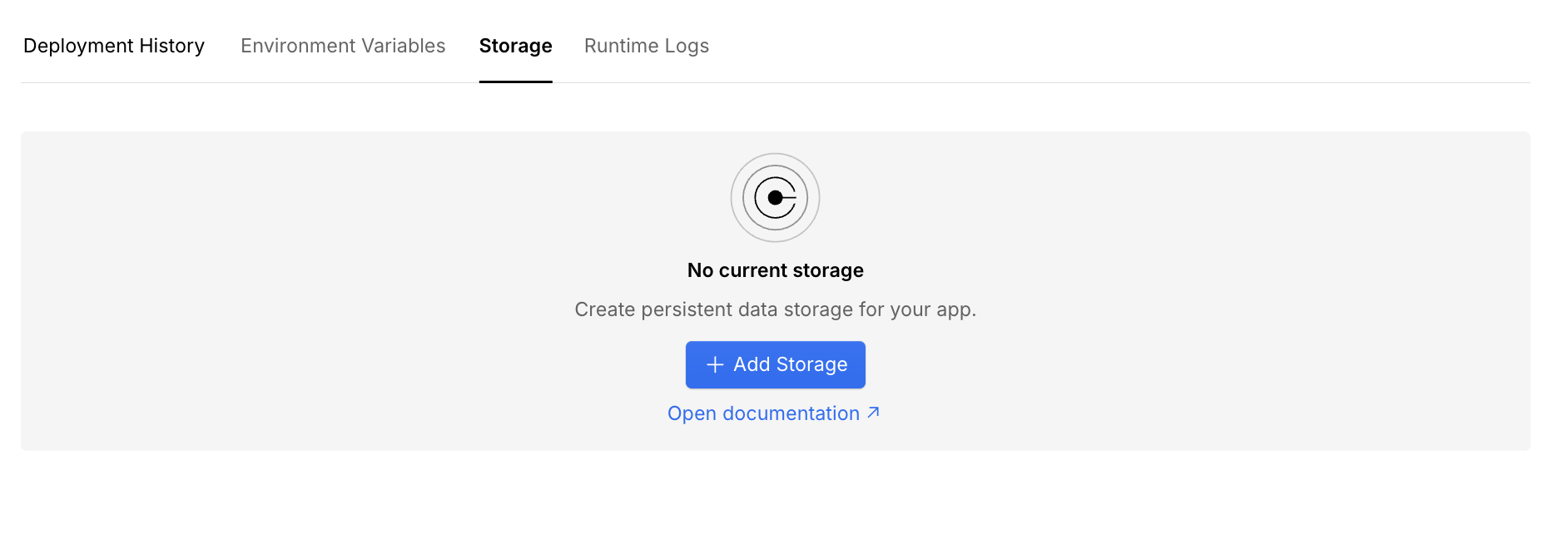
Add a storage resource
Click the Add Storage button to add a new storage resource. Choose the storage type you want to use from the dropdown menu.
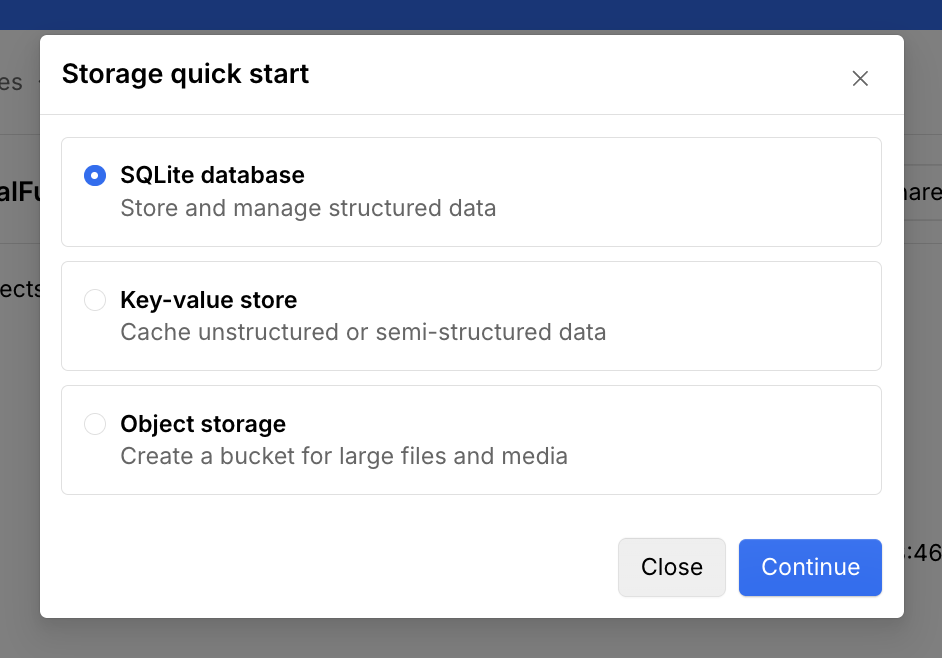
Copy the provided snippet to wrangler.json
Copy the provided snippet, and paste it into the wrangler.json file in your project’s root. Replace the placeholder values with values you want to use.
SQLite
Key Value Store
Object Storage
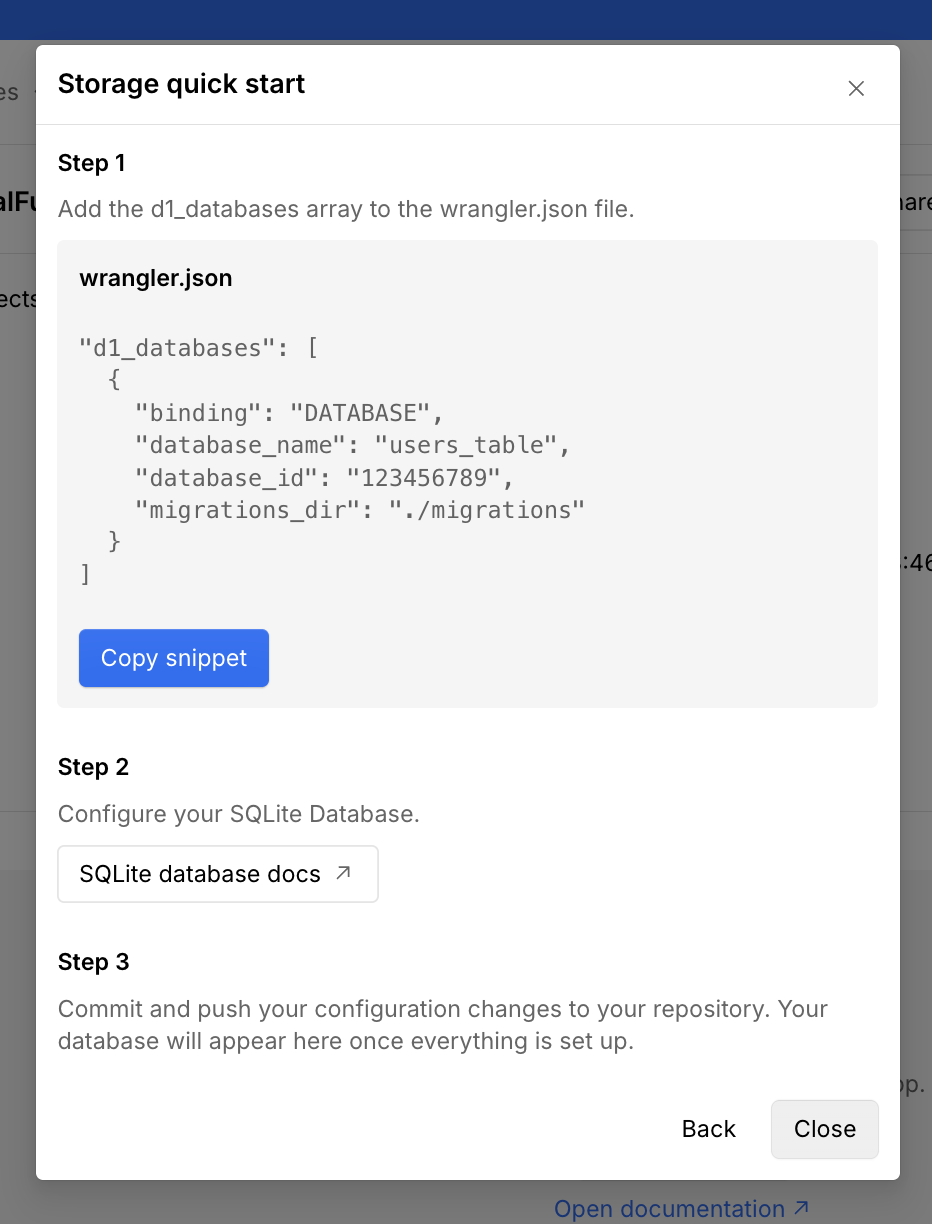
Prepare your database schema
Before deploying your app, you need to prepare your database schema and create a migration file. You can create SQL migration files manually or generate them with a migration tool such as Drizzle ORM. On each deployment, Webflow Cloud will apply the migrations to your database.
Generate types for your binding
Generate TypeScript types for your bindings to enable autocomplete and type safety in your code editor:
This creates/updates a worker-configuration.d.ts file with your binding types.
Deploy your app
Deploy your app to Webflow Cloud by committing and pushing your changes to your linked GitHub repository. After deployment, you can view and manage your storage resources in the Webflow Cloud dashboard.
For a complete walkthrough of using storage in your app, see the guides on adding a SQLite database to your app and adding a Key Value Store to your app.
Accessing storage in your app
Once you’ve declared a binding, access the resource in your app using the binding name as an environment variable. Environment variables for bindings are automatically available in your app and don’t need to be manually created in your environment dashboard.
Next.js
Astro
In a Next.js app, you must access the environment variables for your bindings through the Workers runtime using the getCloudflareContext() function.
How to use getCloudflareContext()
- Always call
getCloudflareContext()inside a function (not at the top level of your module) to ensure the binding is available in the correct context. - For static routes or use outside of request handlers (such as Incremental Static Regeneration or Static Site Generation), use
getCloudflareContext({ async: true })and await the result. This ensures the environment bindings are correctly resolved in all environments.
Managing storage in the Webflow Cloud dashboard
Once you’ve deployed your app with the declared bindings, you can view and manage your storage resources directly in the Webflow Cloud dashboard:
Open the environment dashboard
In Webflow Cloud, select your project and environment where your app is
deployed with storage bindings configured in wrangler.json.
Next steps
- Learn more about SQLite
- Learn more about Key Value Store
- See how to configure storage bindings in your project
- Learn about storage limits in Webflow Cloud
FAQs
Where can I see my storage resources?
Once you’ve deployed your app with the declared bindings, you can view and manage your storage resources directly in the Webflow Cloud dashboard.
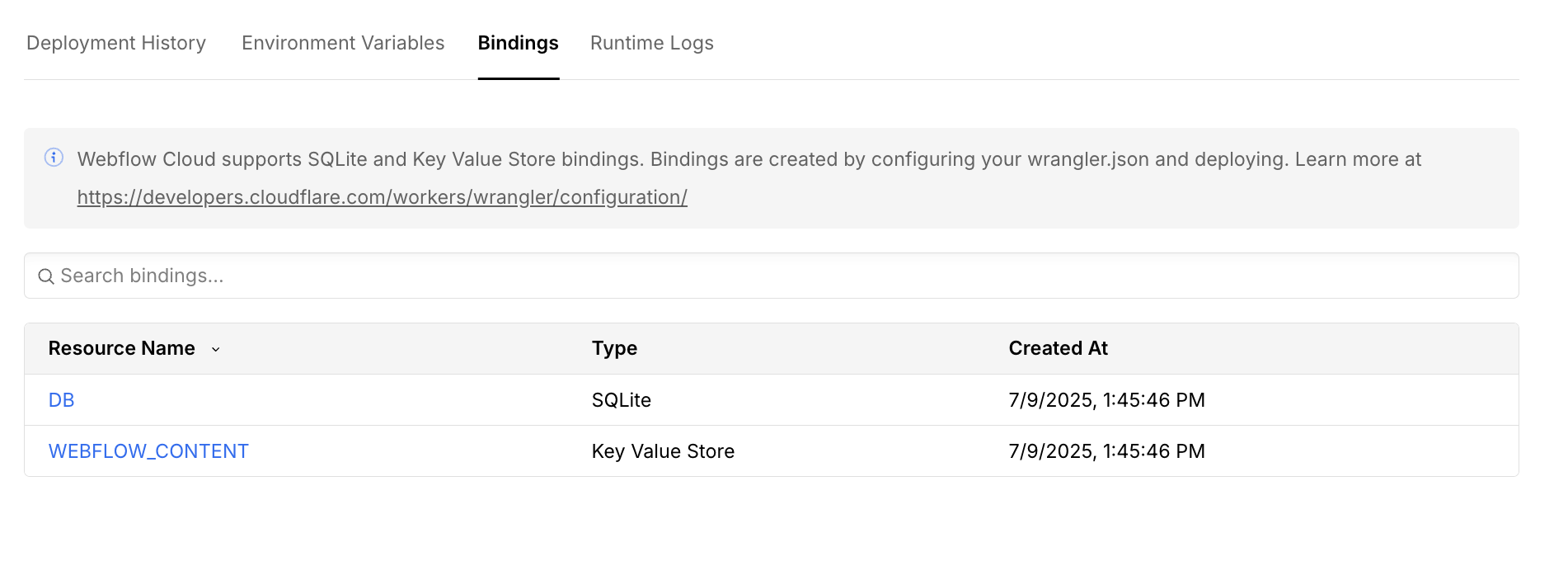
I declared a binding in my wrangler.json file, but I can't see it in the dashboard.
I declared a binding in my wrangler.json file, but I can't see it in the dashboard.
If you have an existing Webflow Cloud project, you may need to edit your project settings to enable storage
- Go to your project in the Webflow Cloud dashboard.
- Select the ”…” icon in the “Actions” section of the menu.
- Select “Edit” (you don’t actually need to edit anything).
- Press “Save Changes” to update your project.

Save the changes and redeploy your app. Once your app deploys you should see the storage tab in the dashboard.
I can't access the API methods on my binding
After declaring a binding, make sure you’ve generated the types for your binding. After running the following command, you’ll be able to access the API methods on your binding.
This creates/updates a worker-configuration.d.ts file with your binding types.